Evaluation by specialists from the Particular Aggressive Research Challenge
EXPERT ANALYSIS — In an period of knowledge overload, the rise of AI and machine studying instruments, and intensifying competitors with China, one query looms giant: Is the U.S. Intelligence Neighborhood (IC) successfully supporting U.S. policymakers? To discover this query, we on the Particular Aggressive Research Challenge (SCSP) carried out an intensive e-survey from 1-25 March 2023. We reached out to 299 present and former nationwide safety officers to guage the intelligence assist they obtained from the U.S. Intelligence Neighborhood throughout their time within the authorities.
A complete of 86 folks took our survey. Of those that took the survey, 27.9% are nonetheless serving within the authorities, 22.1% served as just lately because the final yr, 25.6% within the final three years, and 20.9% within the final 5 years. Those that took the survey included senior leaders (41.9%), managers (20.9%), advisors (25.6%), and analysts (5.8%). The respondents included, amongst others, a Nationwide Safety Advisor, two Deputy Nationwide Safety Advisors, common and flag officers from the varied army providers, together with those that had commanded in fight or held management positions within the European and Indo-Pacific theaters, international service officers, civil servants, and political appointees.
Respondents had expertise working within the government (72.1%), legislative (7%), and judicial (1.2%) branches of the U.S. authorities, in addition to within the army providers (18.6%) and impartial businesses (1.2%). The respondents labored on protection coverage (26%), diplomacy (19%), intelligence issues (16%), commerce (13%), commerce (11%), sanctions (8%), and growth (6%).
KEY FINDINGS
Our survey finds that intelligence stays indispensable to U.S. policymakers. Nevertheless, the intelligence group faces a severe danger of shedding its indispensable position of offering data benefit for choice benefit to U.S. policymakers.
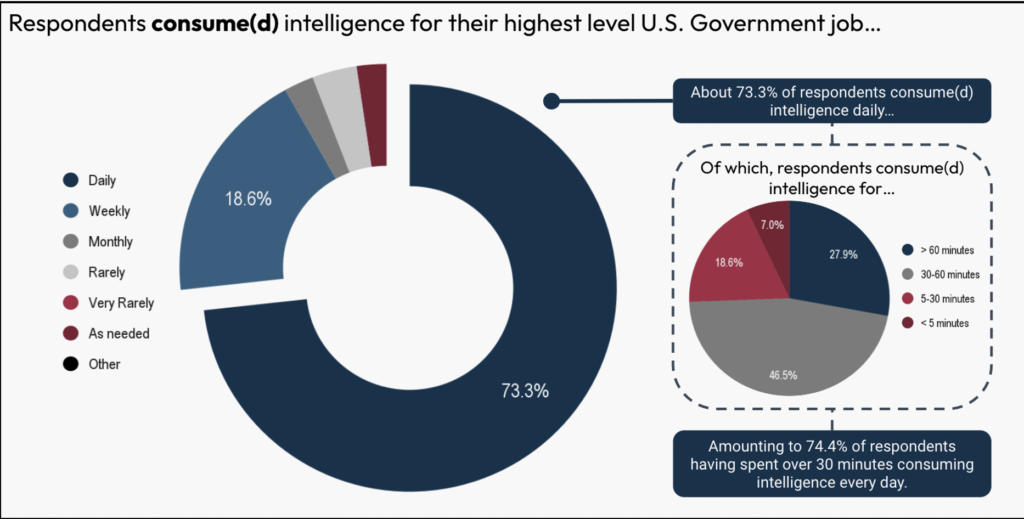
The demand for, consumption of, and satisfaction with intelligence stays exceptionally excessive amongst U.S. policymakers. Almost three quarters of respondents reported consuming intelligence every day and spending half-hour or extra per day consuming intelligence. Importantly, policymakers reported that intelligence influenced their selections significantly and customarily improved coverage outcomes.
On the similar time, practically 1 / 4 of policymakers surveyed indicated that they wished to have obtained higher intelligence to tell coverage outcomes. Almost half of respondents indicated that intelligence solely sometimes impacted their days, with one other 15% noting that it hardly ever impacted their day as policymakers.
Most significantly, the survey reveals that U.S. policymakers are in search of extra fast, accessible, digestible, and instantly related intelligence insights.
- U.S. policymakers seem to rely totally on open sources for many of their every day data wants and breaking information. The vast majority of policymakers mentioned that they relied on open sources for his or her every day data wants, and two thirds mentioned they get breaking information data from open sources.U.S. policymakers seem keen to make use of AI instruments, corresponding to ChatGPT, to generate intelligence insights, viewing such insights as equally good and even superior to human insights, regardless of some suspicion concerning the efficiency of such instruments.
- U.S. policymakers seem to need higher assist from the Intelligence Neighborhood on (a) financial and (b) science and expertise issues, along with the standard assist reported to obtain on politics, army, and strategic choice making.
- And, U.S. policymakers more and more favor the usage of visualizations and digital codecs, in lieu of written reviews and briefings to obtain information and evaluation.
These findings are typically in keeping with the analysis we at SCSP have been conducting over the previous yr. They level to 2 vital conclusions. First, intelligence might be important to the flexibility of U.S. policymakers to realize choice benefit within the technology-charged competitors with China. And, second, the U.S. Intelligence Neighborhood should radically adapt with a view to rise to the event. It should present open supply intelligence, undertake new applied sciences, particularly AI, deliver ahead broader insights, notably on S&T and economics, and design easier-to-digest merchandise. Absent these adjustments, the danger of irrelevance for the U.S. intelligence group is actual.
DETAILED FINDINGS
| Discovering 1: The demand for, consumption of, and satisfaction with intelligence stays exceptionally excessive amongst U.S. policymakers. |
Policymakers have a excessive demand for intelligence, with over 73% of surveyed people consuming it every day. Furthermore, over 74% of respondents spent half-hour or extra per day on intelligence consumption, and practically 28% allotted an hour or extra to it.
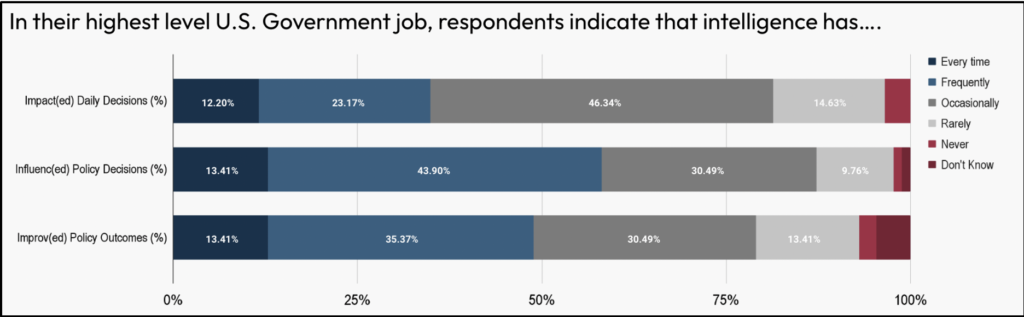
Policymakers reported that intelligence performed a basic position of their work, by influencing their selections significantly and by typically enhancing coverage outcomes. Over 57% of respondents indicated that intelligence influenced their coverage selections both regularly (43.9%) or each time (13.4%). And practically half of respondents (48.8%) thought that intelligence improved coverage outcomes both regularly (35.37%) or each time (13.41%). Intelligence, nevertheless, had much less sway over day-to-day selections, with over 46% of respondents indicating that intelligence sometimes impacted their every day selections; and over 35% indicating that intelligence impacted their every day selections regularly (23.17%) or each time (12.2%).
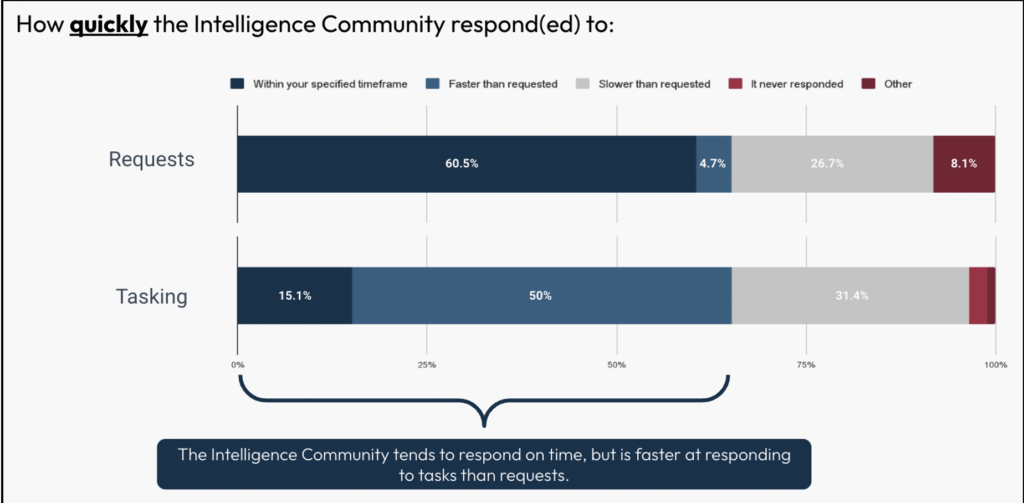
The Intelligence Neighborhood is perceived as being very well timed in addressing policymakers’ calls for, though their responsiveness seems to be a lot quicker for taskings in comparison with requests. Over 65% of the respondents famous that the Intelligence Neighborhood responded to their requests or taskings both on time or quicker than the required deadline. Nevertheless, for requests, solely 4.7% of respondents famous to have obtained a response from the IC quicker than the precise deadline (60.5% nonetheless famous that that they had a response to their request throughout the specified deadline). For taskers, nevertheless, 50% of respondents famous that they obtained their response quicker than the required deadline (and one other 15.1% famous that they obtained their response on time).
| Discovering 2: Policymakers specific a transparent demand for improved IC efficiency. |
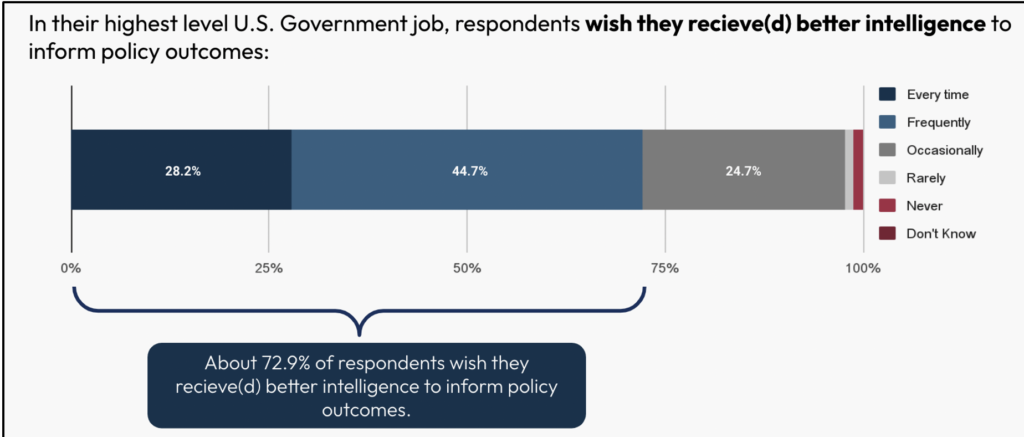
Policymakers see important room for enchancment in assist by the Intelligence Neighborhood. They depend on and acknowledge its worth, however specific a want for added assist. Roughly 72.9% of respondents desired improved intelligence for coverage selections, with 28.2% wanting it each time and 44.7% regularly.
Policymakers flip to the Intelligence Neighborhood principally to grasp the present state of play (27.8%) or to anticipate future developments (26.2%), however considerably much less for particular choice assist (21%) or to question info (18.3%).
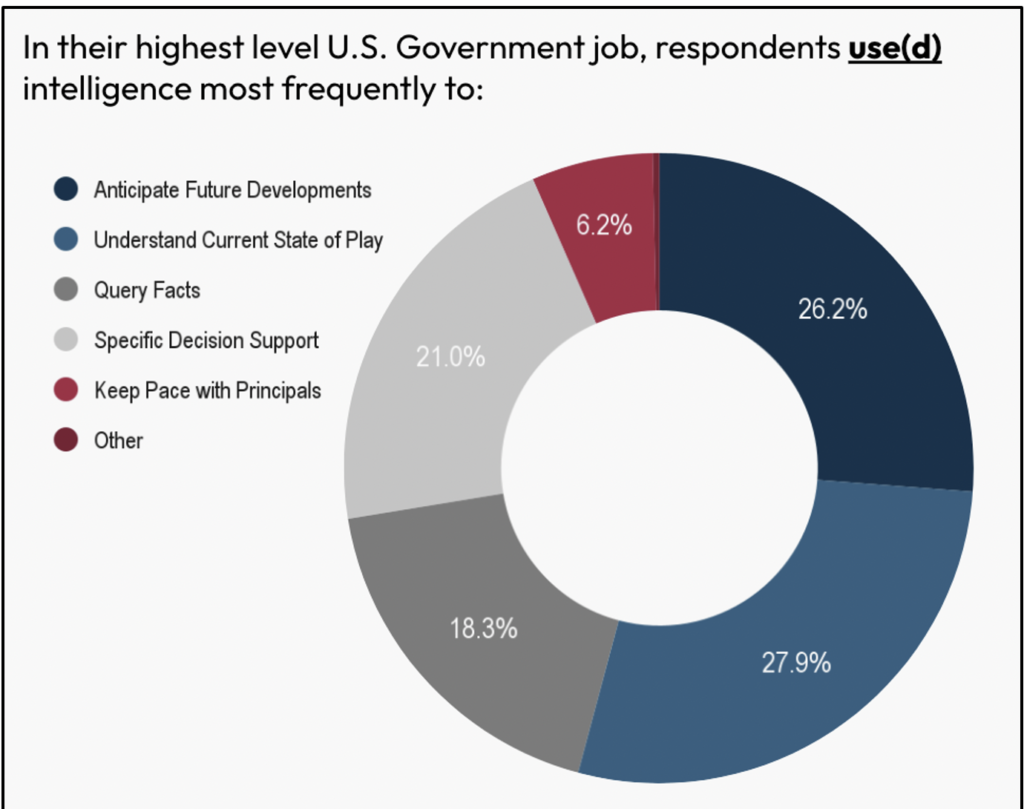
The 2 areas for potential enchancment included evaluation instantly associated to coverage choices and predictive intelligence. Each of those classes confirmed room for enchancment in the case of the amount, high quality, and usefulness of intelligence that policymakers obtained.
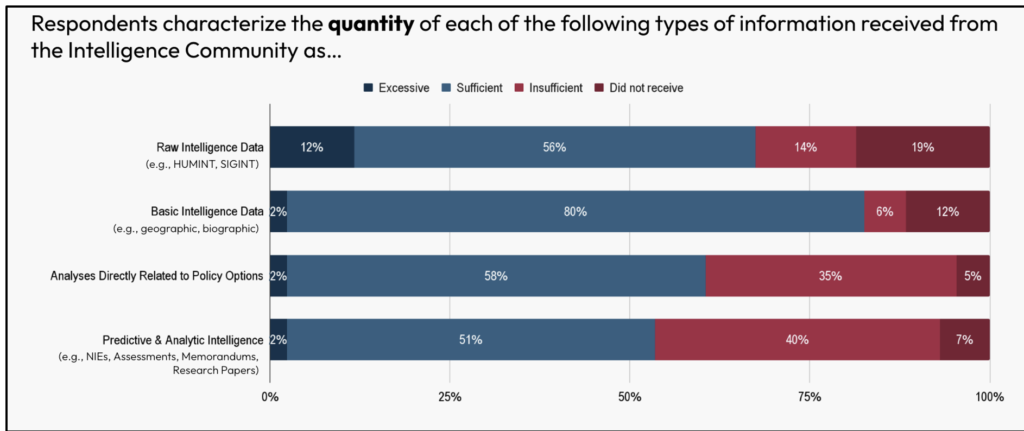
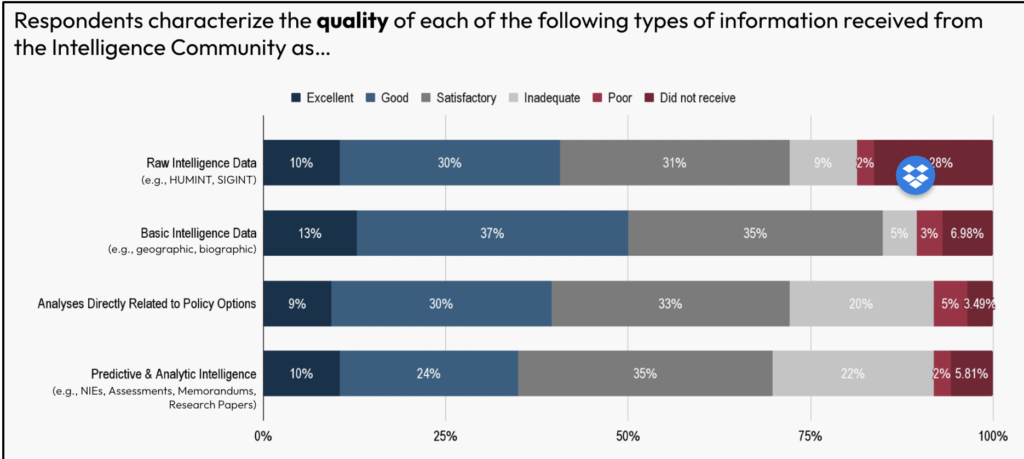
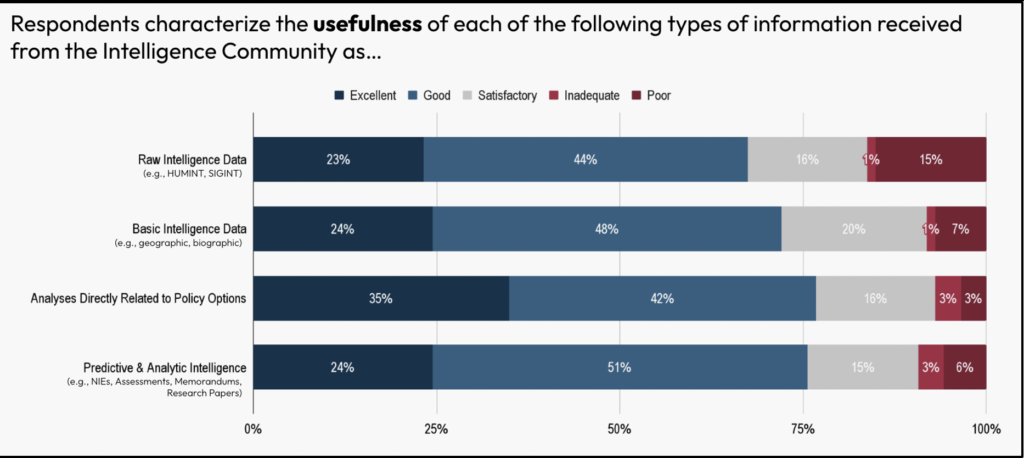
Discovering 3: U.S. policymakers primarily depend on open sources for many of their every day data wants and breaking information.
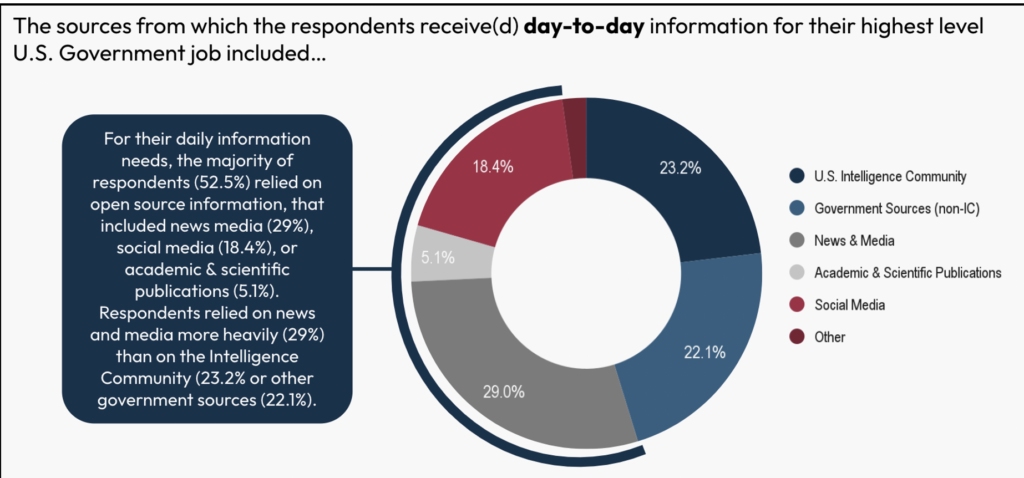
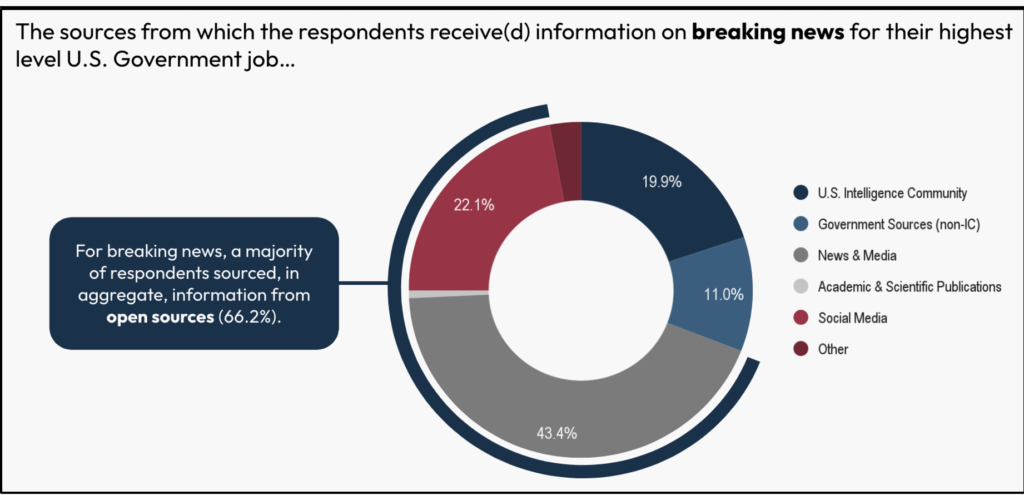
For every day data wants and breaking information, policymakers predominantly use open sources. For every day data consumption, over half (52.5%) relied on information media (29%), social media (18.4%), or tutorial publications (5.1%). Within the survey, they leaned extra on information and media (29%) than the Intelligence Neighborhood (23.2%) or authorities sources (22.1%). For breaking information, two thirds (66.2%) of respondents sourced data from open sources, primarily information and media (43.4%).
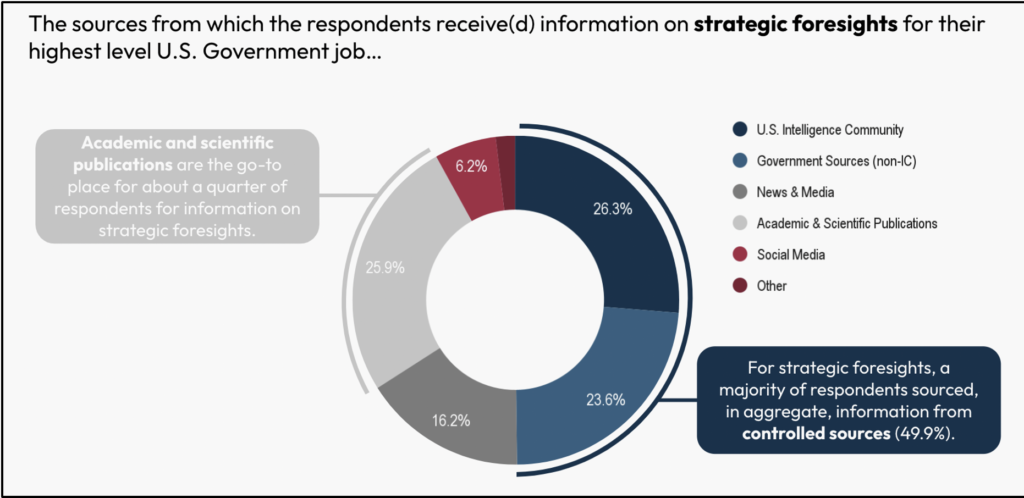
For strategic foresights, nevertheless, a majority of respondents sourced, in mixture, data from managed sources (49.9%), with 26.3% of respondents turning to the Intelligence Neighborhood and one other 23.6% to different authorities sources. Surprisingly, practically 1 / 4 of respondents additionally turned to tutorial and scientific publications for data on strategic foresights.
Discovering 4: U.S. policymakers seem open and even keen to make use of AI instruments, corresponding to ChatGPT, to generate intelligence insights, viewing such insights as equally good and even superior to human insights, regardless of some suspicion concerning the efficiency of such instruments.
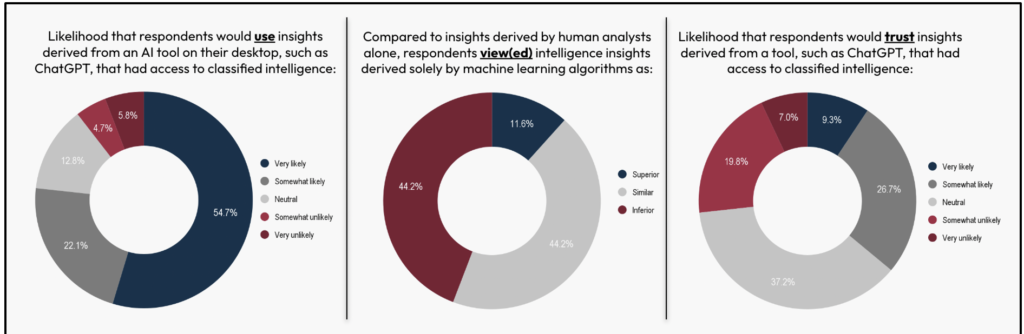
The survey signifies {that a} overwhelming majority of nationwide safety professionals could be keen to make use of AI instruments, corresponding to ChatGPT, to generate intelligence insights, with a majority additionally indicating that they might view such insights are both on par with or superior to these generated by people. Over three quarters of all respondents (76.8%) mentioned that they might be very or considerably seemingly to make use of insights derived from AI instruments with entry to categorised intelligence. The vast majority of respondents (55.8%) indicated that they might view AI-generated intelligence insights as comparable (44.2%) or superior (11.6%) to insights derived by human analysts.
The Cipher Transient hosts expert-level briefings on nationwide safety points for Subscriber+Members that assist present context round at present’s nationwide safety points and what they imply for enterprise. Improve your standing to Subscriber+ at present.
Regardless of the sturdy want to make use of AI instruments for intelligence insights, a good portion of the respondents nonetheless had reservations concerning the high quality of the analytic output from AI instruments and have been considerably break up on whether or not they may totally belief such insights. Over 44% of respondents indicated that they might view AI-generated insights as inferior to these generated by people. On the difficulty of whether or not to belief the AI generated insights, 37.2% of respondents have been impartial, whereas 36% of respondents have been both considerably seemingly (26.7%) or very seemingly (9.3%) to belief AI-generated insights. These conflicted views on the standard of AI generated intelligence insights and whether or not to belief them might be a mirrored image of the truth that instruments corresponding to ChatGPT don’t but exist within the categorised world. Due to this fact, their introduction may shift the attitudes of policymakers – for higher or worse. At a minimal, it appears to point that policymakers would strongly anticipate to see some degree of human-machine teaming within the early days of introduction of AI instruments for intelligence perception era.
| Discovering 5: U.S. policymakers seem to need higher assist from the Intelligence Neighborhood on (a) financial and (b) science and expertise issues, along with the standard assist they obtain on politics, army, and strategic choice making. |
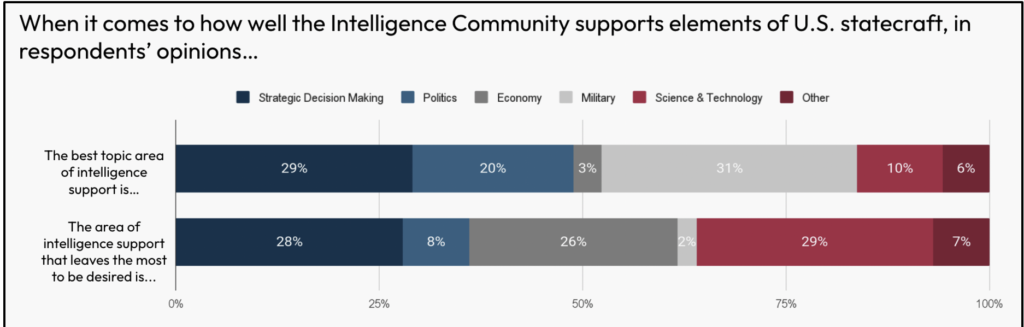
When requested about subjects that the IC does greatest and subjects that it may do higher, the respondents appeared most clearly glad with intelligence assist on subjects corresponding to politics and army issues.
The 2 areas that the respondents desired most enchancment have been financial issues and science and expertise. Solely 3% of respondents felt that financial issues have been the very best space of intelligence assist; and 26% recognized it as an space in clear want of enchancment. Solely 10% of respondents felt that science and expertise have been the very best space of intelligence assist; and 29% recognized it as an space in clear want of enchancment. On one subject – strategic choice making — there was a paradox amongst respondents. Whereas 27% of respondents felt it was a subject on which the IC excels, 28% of respondents additionally recognized it as a subject on which the IC may enhance essentially the most.
Discovering 6: U.S. policymakers look like growing a desire for visualization of knowledge and evaluation, and digital format normally, in lieu of written reviews and briefings.
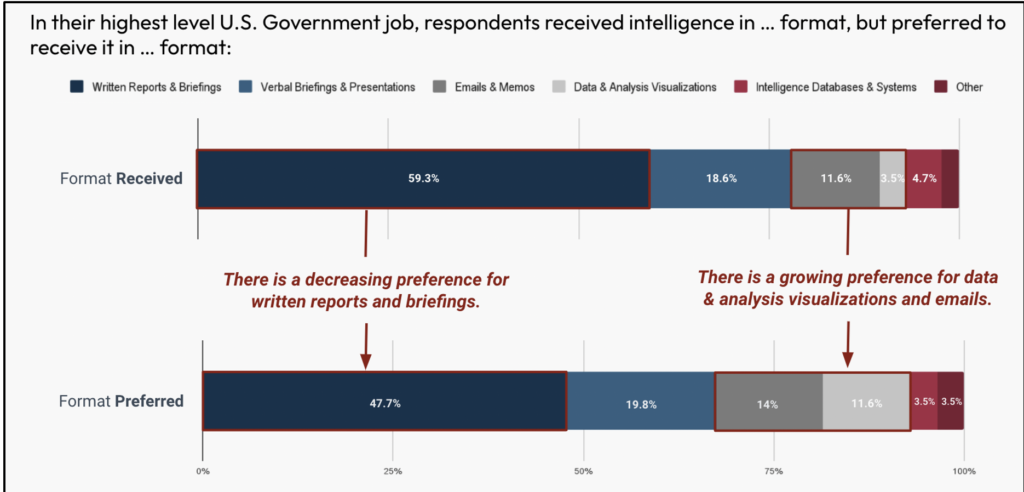
With respect to the format of intelligence merchandise, the IC continues to push its merchandise primarily in written format or by way of briefings. Nevertheless, the policymakers look like growing a stronger desire for information and visualization and emailed merchandise.
Respondents indicated that of the totality of intelligence data they obtained, practically 60% was obtained in writing or by way of briefings.
When requested how they wished that they had obtained their intelligence merchandise, written merchandise and briefings constituted solely 47.7% of the format. The desire for electronic mail submissions elevated from 11.6% to 14%, and the desire for visualization elevated from 3.5% to 11.6%.
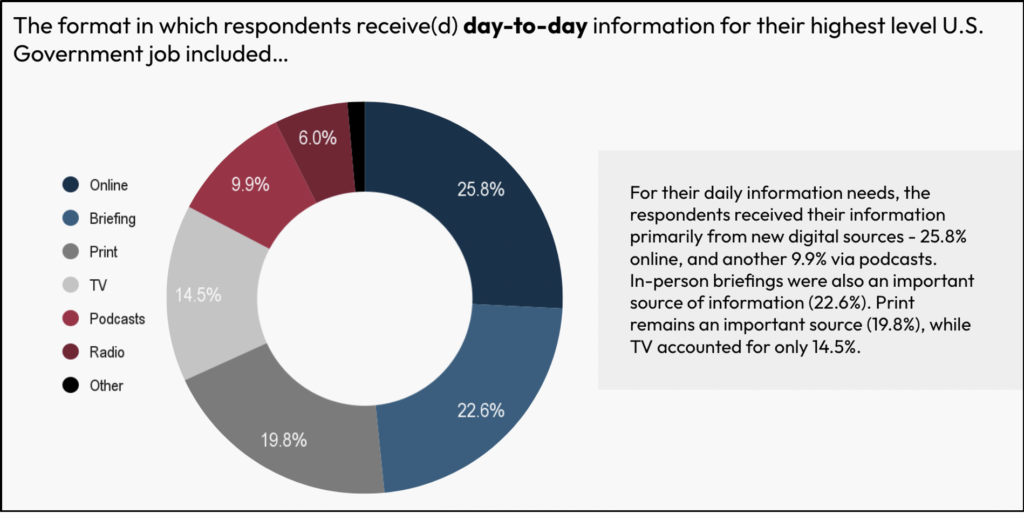
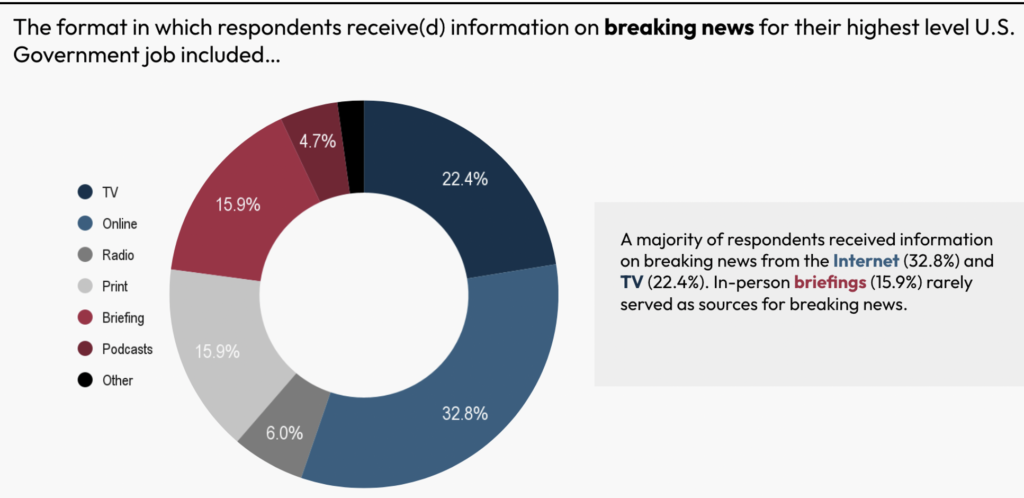
For his or her every day data wants, the surveyed policymakers obtained their data primarily from new digital sources – 25.8% on-line, and one other 9.9% by way of podcasts. In-person briefings have been additionally an vital supply of knowledge (22.6%). Print stays a supply (19.8%), whereas TV accounted for 14.5%. A majority of respondents obtained data on breaking information from the Web (32.8%) and TV (22.4%). In-person briefings (15.9%) served a restricted position as a supply for breaking information.

FINAL THOUGHTS
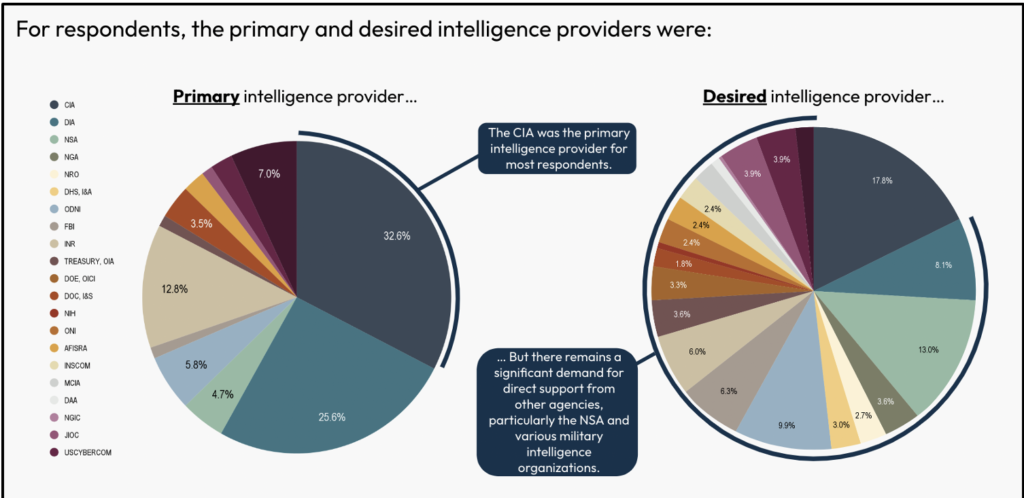
Amongst these surveyed, three intelligence entities have been the first suppliers of intelligence – CIA (32.6%), DIA (25.6%), and INR (12.8%), respectively. When requested who they might have most well-liked to have been their intelligence supplier, all three entities skilled a substantial decline. Alternatively, respondents’ preferences for entities corresponding to NSA, DNI, and army intelligence organizations grew considerably.
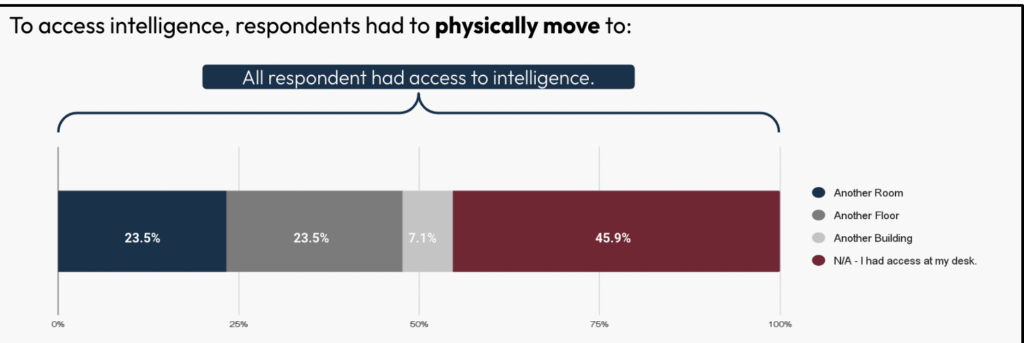
Bodily entry to intelligence stays a difficulty. The vast majority of respondents (54.1%) needed to go away their desks for one more room, ground, or constructing altogether to entry intelligence. Lower than half of the respondents (45.9%) didn’t have to depart their desk to entry intelligence. These numbers have been shocking, since practically 42% of the respondents reported having labored as senior leaders and one other 21% as managers within the authorities. Almost 1 / 4 of respondents needed to go to a different room to entry intelligence, and one other quarter needed to go to a different ground, with over 7% having to go to a different constructing to entry intelligence.
LIMITATIONS
It is very important word potential biases in these outcomes, together with nonresponse bias, as not all invited members accomplished the survey. This may increasingly result in an over- or underrepresentation of sure views or experiences. Furthermore, members who’re now not serving within the authorities could also be topic to hindsight bias, doubtlessly influencing their recollection of occasions and experiences.
The survey was completely administered by way of Google Varieties, limiting participation to these with entry to Google providers and suitable electronic mail platforms. Consequently, not all people, notably these working in managed environments, may entry and full the survey. This restriction could have impacted the general representativeness of the survey outcomes.
The pattern for this evaluation is restricted to policymakers with whom SCSP workers have both engaged or interacted with beforehand.
The Cipher Transient is dedicated to publishing a variety of views on nationwide safety points submitted by deeply skilled nationwide safety professionals.
Have a perspective to share primarily based in your expertise within the nationwide safety subject? Ship it to [email protected] for publication consideration.
Learn extra expert-driven nationwide safety insights, views and evaluation in The Cipher Transient as a result of Nationwide Safety is Everybody’s Enterprise









