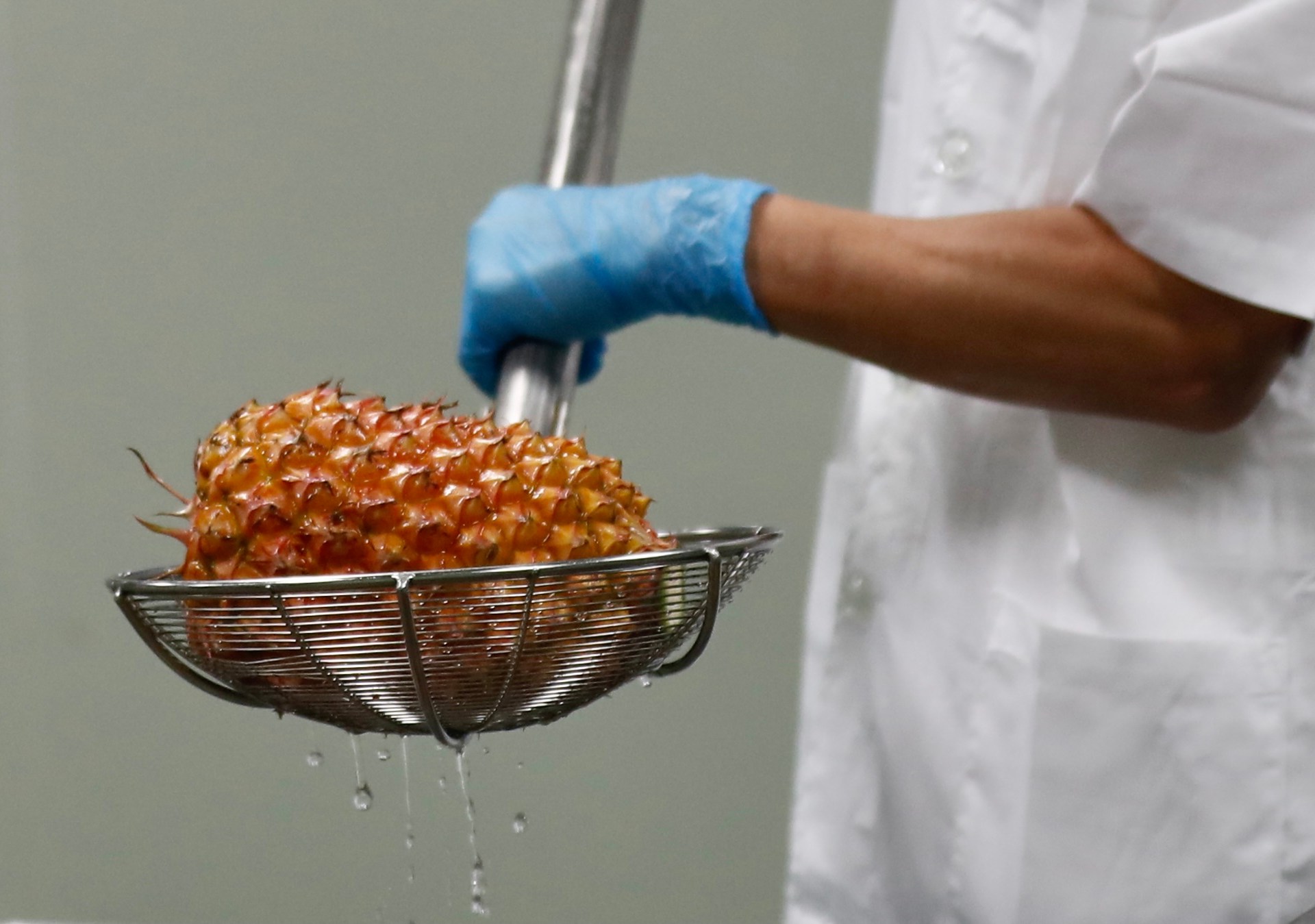
Taipei, Taiwan – In early 2021, Chien and his fellow pineapple farmers in southern Taiwan acquired dangerous information: China had added their crop to a listing of banned imports, claiming considerations about pests and different issues of safety.
On the time, Taiwanese pineapple farmers have been sending practically all their fruit to China in an business value $284m a 12 months, even after factoring within the COVID-19 pandemic. Inside a month, the worth of their pineapples had dropped from 60 US cents per 600gm to mere pennies, in response to Chien.
“As quickly because the information broke, the entire thing collapsed inside a month,” he mentioned, asking to not use his full title for worry of financial repercussions as a result of he sells pineapples to Hong Kong.
Worse nonetheless, the not too long ago harvested crop couldn’t be offered regionally or exported to neighbours like Japan and Hong Kong due to points over product high quality, he added.
“Taiwan had probably not promoted export merchandise as a result of they relied on China up to now. Farmers have been very nervous in regards to the political scenario, and the worth of pineapples was very low as a result of they might not promote them,” he instructed Al Jazeera.
Beijing, which claims Taiwan as its personal territory, introduced extra bans over the following months, concentrating on different tropical fruits equivalent to candy custard-like sugar apples and crunchy pear-shaped wax apples.
For observers in Taiwan, the import bans had little to do with meals security or considerations about pesticides. It seemed to be one other case of Beijing expressing its anger on the governing Democratic Progressive Social gathering (DPP), which it regards as “separatist” and hell-bent on independence.
‘Clear correlation’
Because the DPP took energy in 2016 beneath President Tsai Ing-wen, Beijing has resorted to numerous technique of coercion to undermine her authorities, together with navy workouts within the Taiwan Strait, selecting off Taiwan’s previous couple of diplomatic allies, stirring up misinformation campaigns on-line, and isolating the self-ruled island from worldwide organisations.
Beijing has additionally turned to financial coercion, banning particular person vacationers from visiting Taiwan in 2019, fining Taiwanese firms working in China equivalent to Far Jap Group in 2021, and inserting import bans on Taiwanese merchandise from fruits to fish.
Hitting out at Taiwanese farmers like Chien has restricted financial influence on Taiwan’s financial system, however the message is evident to Taiwan watchers.
Most farmers dwell in southern Taiwan, a stronghold of the DPP. In August 2022, China banned greater than 2,000 Taiwanese imports, together with biscuits and pastries, in protest in opposition to a historic go to to Taiwan by then-US Speaker of the Home of Representatives Nancy Pelosi.
These efforts have continued within the lead-up to Taiwan’s presidential and legislative elections on January 13. As marketing campaign season kicked off final April, Beijing introduced a significant investigation into Taiwanese commerce practices, ruling final month that Taiwan had unfairly imposed “commerce limitations” on greater than 2,000 Chinese language merchandise.
“This timeline aligns completely with Taiwan’s presidential election. There appears to be a transparent correlation indicating China’s intention to leverage commerce points as bargaining chips to affect Taiwan’s voters’ mistrust within the DPP’s governance and reduce their credibility in dealing with cross-Strait commerce conflicts,” wrote Chun-wei Ma, an assistant professor for worldwide affairs at Tamkan College, in a latest report on the problem.
The goal is to encourage voters to maneuver away from presidential candidates just like the DPP’s William Lai and in the direction of a extra “China-friendly” celebration, Ma mentioned.

Taiwan’s authorities has additionally accused Beijing of election interference by means of financial coercion, equivalent to when it ended tariff cuts on a dozen Taiwanese petrochemical imports in late December – simply as voters have been beginning to make their ultimate choices.
Related allegations have been made when Beijing focused Apple provider Foxconn with a shock tax investigation in November in what was broadly seen as a rebuke of founder Terry Gou’s choice to run for president.
The transfer was additionally criticised as “political” by Taiwan’s Nationwide Safety Council, as Beijing didn’t need Gou to divide the opposition within the upcoming election, elevating the prospect of a DPP victory, in response to division head Wellington Koo.
The extra conservative Kuomintang (KMT), in distinction, has an extended working relationship with Beijing. The impartial Taiwan Folks’s Social gathering has additionally known as for extra cooperation and renewed talks on a controversial service commerce settlement with China.
Nonetheless, regardless of Beijing’s flurry of exercise, Taiwan consultants equivalent to Bonnie Glaser, managing director of the Indo-Pacific Program on the German Marshall Fund, argue its financial coercion stays restrained and largely symbolic in contrast with the injury it may probably inflict.
With cross-strait commerce valued at $205bn in 2022 in response to Taiwanese knowledge, China is Taiwan’s largest buying and selling companion – a place that holds no small affect. Beijing has proven that it’s not afraid to punish different shut commerce companions – in 2021 it minimize off coal and different imports from Australia, for example, after Canberra known as for an impartial investigation into the origins of COVID-19.
“Not like the instances of Australia, South Korea and different international locations which have been meant to punish and to discourage others from difficult Chinese language pursuits, financial stress on Taiwan has been small-scale and a part of a broader technique of stopping Taiwan independence and selling reunification,” Glaser instructed Al Jazeera by electronic mail.
Analysts notice that Beijing has but to focus on Taiwan’s all-important semiconductor business, the world’s largest, or the landmark 2010 Cross-Strait Financial Cooperation Framework Settlement, which minimize tariffs on main imports and exports.
Glaser feels Beijing’s financial coercion is prone to have essentially the most influence on undecided voters.
“The usage of financial coercion to affect Taiwan’s elections is barely one of many instruments that Beijing is utilizing,” she mentioned. “It’s unlikely to have any influence on voters who’re the bottom for the [KMT] and [DPP] or those that have already determined who they are going to vote for. However it could have some influence on undecided voters.”
New technology of voters
Whereas China depends on previous strategies to sway voters, Taiwan’s voter base is altering.
Voters born in the direction of the top of martial legislation and later see themselves as Taiwanese and never Chinese language are uninterested in their overbearing neighbour to the north and its punishment for asserting their identification.
They’ve additionally grown up in a way more secure atmosphere than a few of their dad and mom and grandparents. They might have missed the financial increase of the Seventies and 80s, however additionally they grew up with an general greater lifestyle with advantages like medical health insurance and widespread greater training.
Austin Wang, who research Taiwanese public opinion on the College of Nevada, Las Vegas, mentioned China’s coercive actions have begun to backfire at a transitional second for Taiwan.
“Financial profit from China certainly influenced the general public opinion in Taiwan up to now,” he mentioned.
“The elder technology who skilled poverty cared in regards to the financial system greater than identification. Nonetheless, for the reason that youthful technology in Taiwan entered the period of post-materialism, financial advantages can hardly change their identification or angle towards independence.”
As Taiwan’s political panorama adjustments, its financial presence in China can be falling. Thanks partially to the pandemic, the inhabitants of Taiwanese individuals working in China fell from a excessive of 261,000 in 2011 to a low of 163,000 in 2021, in accordance to authorities knowledge.
Some companies working there additionally questioning the longer term.
A 2022 survey of 500 Taiwanese firms by the US Middle for Strategic and Worldwide Research (CSIS) revealed that whereas 60.8 p.c of respondents had enterprise operations in China, 76.83 p.c felt Taiwan wanted to scale back its “financial dependence on China”.
1 / 4 of respondents mentioned that they had already moved a few of their enterprise out of China, and a 3rd have been contemplating transferring some operations.

On the bottom in Taiwan, even farmers are having related ideas.
Beijing reversed its ban on Taiwanese pineapples in 2023, nevertheless it was additionally a lesson in why they wanted to scale back their dependence on China.
Throughout the three years they have been locked out of the Chinese language market, farmers labored collectively, and with the federal government, to develop higher high quality pineapples that might be exported to extra demanding markets in Hong Kong and Japan, farmer Chien defined.
As enterprise and costs rise, Chien mentioned older farmers might return to enterprise as traditional, however the youthful technology won’t overlook what occurred.
“We don’t need to be used as bargaining chips. As a result of even when it’s nice at this time, even when the [Chinese market] was changed, and a unique president was chosen, the scenario would nonetheless not change,” he mentioned. “If China is sad, we may nonetheless be cancelled or banned, in order that’s a really unhealthy commerce relationship.”









